How Big Is a Baby at 6 Weeks? Having a baby at 6 weeks is a fantastic experience and a dream for many mothers. Despite the excitement, however, there are still many questions you may have about your pregnancy. These include how big is a baby at 6 weeks, when is a baby’s due date, and what are some pregnancy symptoms?
Mood swings
Mood swings are a normal part of pregnancy. The hormones involved can have a dramatic effect on your mood and may even lead to some pretty dramatic bouts of depression.
The best thing to do if you are experiencing mood swings is to consult a physician. They can provide you with treatment options for mild and moderate cases, as well as more serious cases.
There are many ways to combat mood swings during pregnancy. Among them are taking a daily multivitamin, eating a healthy diet, and engaging in some light exercise.
Morning sickness
During the first trimester, nausea and fatigue can be especially difficult. Many expectant moms find relief with prenatal vitamins, certain foods, and certain beverages.
While it may be impossible to know how big a baby is at 6 weeks with morning sickness, the symptoms will generally subside by the time the second trimester rolls around. It’s also important to know that morning sickness isn’t harmful to either the baby or the mother.
In the first trimester, the embryo’s heart isn’t yet fully developed. It’s roughly the size of a poppy seed. It’s also still in the process of forming a four chamber organ.
Skin swelling
During your 6th week of pregnancy, the baby is growing quickly. It is measuring roughly 0.04 inches long and 0.25 inches wide from crown to rump. The size of the uterus is also relatively consistent at this point.
It is not uncommon for a woman to experience cramping during her 6th week of pregnancy. Although not all cramps are serious, they should be treated as a medical emergency.
The tadpole-like embryo that is growing in your uterus is forming many features, including a chin, cheeks, eyes, and a tail. It has also started to develop teeth and a spinal cord.
Organogenesis
During the first two weeks of pregnancy, the embryo begins to form. This is a critical period of development as the internal and external structures of the body are formed. These structures give rise to all of the organs of an infant.
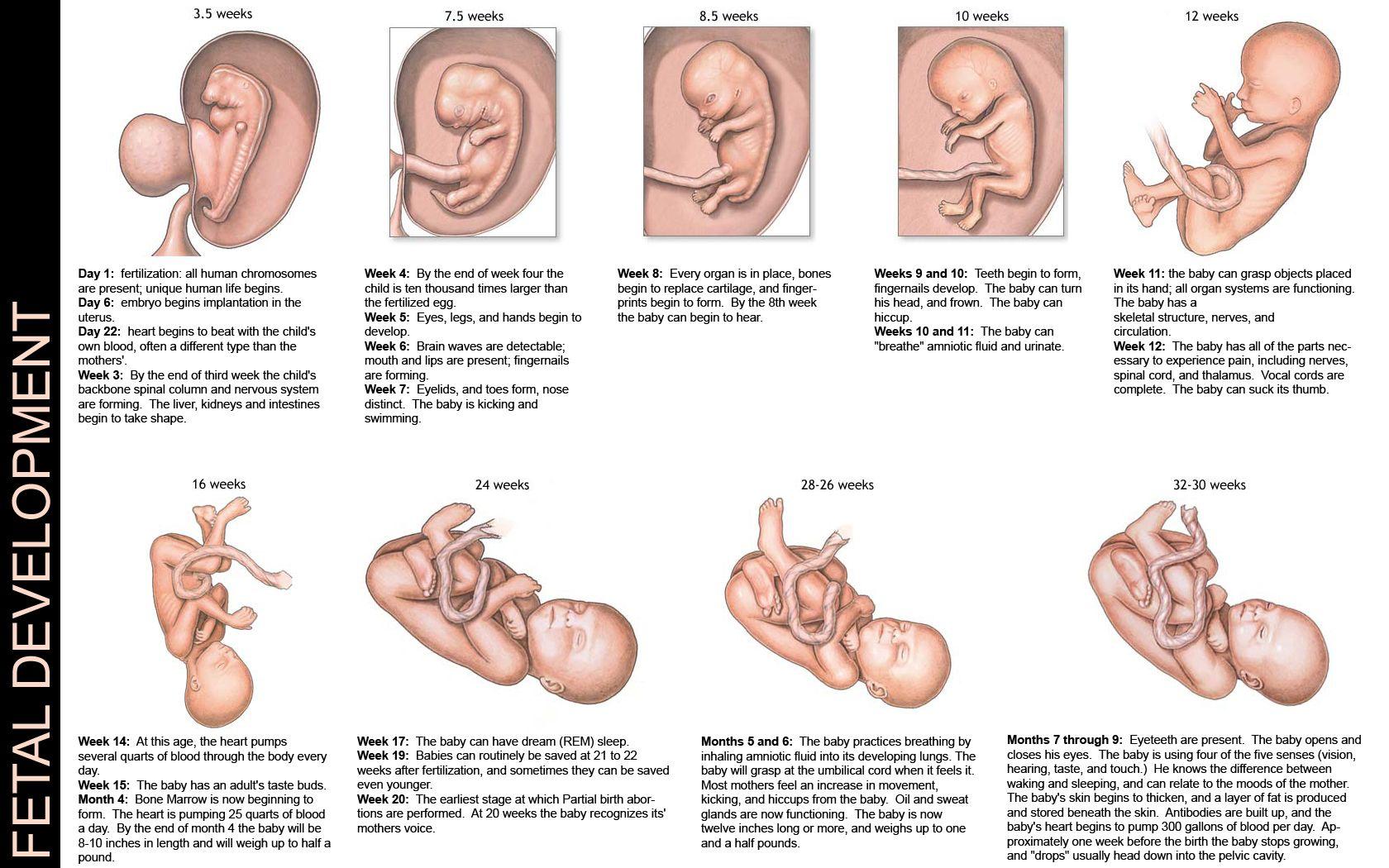
At the end of the first week, the embryo forms a three-layered disc. This disc consists of a central membrane, a lateral membrane, and an outer membrane. The outer membrane forms the trophoblast. The trophoblast gives rise to the placenta. The placenta supplies the fetus with nutrition and excretion. It also removes carbon dioxide from the mother’s blood and transfers oxygen and nutrients to the fetus.
Folic acid
Getting the right amount of folic acid can prevent birth abnormalities and pregnancy loss. Folic acid helps to prevent neural tube defects, which affect the baby’s brain, spinal cord, and other body parts. These defects occur before a person is aware that they are pregnant.
Folic acid should be taken before conception and during the first trimester. The CDC recommends taking 400 micrograms of folic acid daily. If you are taking medications or if you have a genetic condition, you may need to take a higher dose.
Folic acid may also reduce the risk of birth defects and preterm labor. A study of women in their first year of pregnancy found that those who took folic acid cut their risk of delivery by 50%. If you want to get pregnant, talk to your doctor about how much folic acid you need to take each day.
Calcium, iron and vitamin D
During pregnancy, it is important to get enough iron and calcium. These nutrients are vital for developing strong bones. They also help build blood cells and carry oxygen to your baby. If your baby does not get enough iron, he will have low energy and become tired.
Vitamin D is also important during pregnancy. It helps absorb proteins and new blood cells. It can also help prevent neural tube defects.
Vitamin D supplements should be started early on. Calcium and iron are essential for your baby’s bones and teeth. There are many prenatal vitamins on the market that contain the right amounts of each. Some also contain folic acid, which is also important during pregnancy.
Prenatal checkups are usually at 8 or 9 weeks
During your pregnancy, you will need to visit a health provider on a regular basis. Prenatal checkups are important because they will provide you with important information about the health of your baby.
Prenatal checkups are usually scheduled around 8 or 9 weeks of pregnancy. At these visits, your healthcare provider will do a complete physical exam to look for health problems. The provider will also go over healthy eating and exercise habits. Your provider may also order tests.
A health provider will likely perform blood and urine tests to check your blood count, red blood cell count, platelet count, and Rhesus factor. This is important because anemia is common among pregnant women. Low hemoglobin and hematocrit levels indicate that you don’t have enough healthy blood cells to carry oxygen. Various blood tests can also be used to test for certain infections and immune deficiencies.